 |
 |
- Search
| J. KIMS Technol > Volume 24(5); 2021 > Article |
|
Abstract
Cyber threats can bypass existing cyber-protection systems and are rapidly developing by exploiting new technologies such as artificial intelligence. In order to respond to such cyber threats, it is important to improve the ability to detect unknown cyber threats by correlating heterogeneous cyber protection systems. In this paper, to enhance cyber-attack response capabilities, we proposed command and control that enables rapid decision-making and response before the attack objectives are achieved, using Lockheed Martin's cyber kill chain and MITRE ATT&CK to analyze the purpose and intention of the attacker.
ņ¦ĆĻĖł ņÜ░ļ”¼ ņé¼ĒÜīļŖö ļ¬©ļōĀ Ļ▓āņØ┤ ņé¼ļ¼╝ņØĖĒä░ļäĘ(IoT)ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņŚ░Ļ▓░ļÉśņ¢┤ ņŗ£Ļ░äĻ│╝ ņןņåīņŚÉ ĻĄ¼ņĢĀļ░øņ¦Ć ņĢŖĻ│Ā ņøÉĒĢśļŖö ņĀĢļ│┤ļź╝ Ēü┤ļØ╝ņÜ░ļō£(Cloud)ņŚÉ ļ│┤Ļ┤ĆĒĢśņśĆļŗżĻ░Ć ņ¢ĖņĀ£ļōĀņ¦Ć ļČłļ¤¼ņś¼ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ļśÉĒĢ£ ņØĖĻ│Ąņ¦ĆļŖź(AI)ņØä ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ╣ģļŹ░ņØ┤Ēä░ ĻĖ░ņłĀņØä ļłäĻĄ¼ļéś ņåÉņēĮĻ▓ī ņØ╝ņāüņāØĒÖ£ņŚÉņä£ ĒÖ£ņÜ®ĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż. ņé░ņŚģĒśäņןļÅä ņŗżņĀ£Ļ│ĄĻ░äĻ│╝ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓äĻ│ĄĻ░äņØś ņĀĢļ│┤Ļ░Ć ņ¦ü ┬Ę Ļ░äņĀæņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ│Ąņ£ĀļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŖö ņĀ£4ņ░© ņé░ņŚģĒśüļ¬ģ ņŗ£ļīĆņŚÉ ņé┤Ļ│Ā ņ׳ņ£╝ļ®░, Ļ│ĄĻ│Ą ┬Ę ļ»╝Ļ░äĻĖ░Ļ┤Ć, ĻĄŁļ░® ļō▒ ĒŖ╣ņĀĢ ņśüņŚŁņŚÉ ĻĄ¼ļČäņŚåņØ┤ ĻĄŁĻ░Ć ņĀäļ░śņŚÉņä£ ļööņ¦ĆĒäĖĒÖöĻ░Ć ĒÖĢņé░ļÉśņŚłļŗż. ļ¬©ļōĀ ņŻ╝ņ▓┤ņØś ĒÖ£ļÅÖ ĻĖ░ļ░śņØ┤ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓äĻ│ĄĻ░äņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒÖĢļīĆļÉ©ņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņØ┤ ņ¦ĆļŖźĒÖö ┬Ę Ēæ£ņĀüĒÖö ┬Ę Ļ│ĀļÅäĒÖö ┬Ę ņĪ░ņ¦üĒÖöļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢ┤ Ļ░£ņØĖ, ĻĖ░ņŚģņØä ļäśņ¢┤ ĒĢ£ ļéśļØ╝ņØś ĻĄŁĻ░Ć ņĢłļ│┤Ļ╣īņ¦Ć ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņżä ļ¦īĒü╝ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ£äĒśæņØ┤ ņŗ¼Ļ░üĒĢśĻ▓ī ņ”ØĻ░ĆĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż[1]. ņĄ£ĻĘ╝ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņØĆ Ēśäņ×¼ ņÜ┤ņÜ®ņżæņØĖ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ļ░®ĒśĖņ▓┤Ļ│äļź╝ ņÜ░ĒÜīĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ļŖźļĀźņØä ļ│┤ņ£ĀĒĢ£ Ļ░ĆņÜ┤ļŹ░ ņØĖĻ│Ąņ¦ĆļŖź(AI) ļō▒ ņŗĀĻĖ░ņłĀņØä ņĢģņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ¦ĆļŖźĒÖöļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż. ĻĖłņĀä ļ░Å ņĀĢļ│┤ ĒāłņĘ© ļ¬®ņĀüņØś Ēæ£ņĀüĒÖöļÉ£ ļ×£ņä¼ņø©ņ¢┤ņÖĆ ņé¼ĒÜīņĀü, ņŗ£ĻĖ░ņĀü ņØ┤ņŖłļź╝ ĒÖ£ņÜ®ĒĢ£ Ļ│ĀļÅäĒÖöļÉ£ Ēö╝ņŗ▒ ļ░Å ņŖżļ»Ėņŗ▒ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņŗĀņóģ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ£äĒśæņØ┤ ņĪ░ņ¦üĒÖöļÉśņ¢┤ ļīĆņØæņØś ņ¢┤ļĀżņøĆņØĆ ļéĀļĪ£ ņ”ØĻ░ĆĒĢśĻ│Ā ņĢīļĀżņ¦Ćņ¦Ć ņĢŖņØĆ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ£äĒśæņŚÉļÅä ļģĖņČ£ļÉśņ¢┤ ņ׳ļŗż[2]. ņØ┤ņŚÉ ņĀĢļČĆņŚÉņä£ļŖö 2019ļģä 4ņøö, ŌĆśĻĄŁĻ░Ć ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓äņĢłļ│┤ ņĀäļץŌĆÖņØä ņłśļ”ĮĒ¢łņ£╝ļ®░, ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļīĆņØæņŚŁļ¤ēņØä Ļ│ĀļÅäĒÖöĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓äņĀä ļīĆļ╣ä ņĀäļץ ┬Ę ņĀäņłĀņØä Ļ░£ļ░£ĒĢśĻ│Ā ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņĀäļĀźņ▓┤Ļ│ä ļ│┤Ļ░Ģ ņŚģļ¼┤ļź╝ ņČöņ¦äĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż. ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņĀäļĀźņ▓┤Ļ│äņØś ļ│┤Ļ░ĢņØä ņ£äĒĢ┤ņä£ļŖö ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ļ░®ĒśĖĻĖ░ļŖźņØä ļČäņäØĒĢśņŚ¼ ņäĀņĀ£ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ£äĒśæņØä ņśłņĖĪĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ļīĆņØæņŚŁļ¤ēņØ┤ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢśļŗż.
ļö░ļØ╝ņä£, ļ│Ė ļģ╝ļ¼ĖņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņĀäļĀźņ▓┤Ļ│äļź╝ Ļ░ĢĒÖöĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ£ ļ░®ņĢłņ£╝ļĪ£ ļĪØĒ׳ļō£ļ¦łĒŗ┤ņØ┤ 2011ļģäņŚÉ ļ░£Ēæ£ĒĢ£ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ēé¼ ņ▓┤ņØĖ(Cyber Kill Chain)[3]Ļ│╝ MITRE ATT&CK(Adversarial Tactics, Techniques and Common Knowledge) ļō▒ņØś Ļ▓Ćņ”ØļÉ£ ļ¬©ļŹĖņØä ņĀüņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ Ēśäņ×¼ ņÜ┤ņÜ®ņżæņØĖ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ļ░®ĒśĖņ▓┤Ļ│äņØś ĒĢ£Ļ│äņĀÉņØä ļÅäņČ£ĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ļŗ©Ļ│äļ│ä ļīĆņØæņ▒ģņØä Ļ▓ĆĒåĀĒĢśĻ│Āņ×É ĒĢ£ļŗż. ļśÉĒĢ£ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņ×ÉņØś ļ¬®ņĀüĻ│╝ ņØśļÅäļź╝ ĒīīņĢģĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ļ░®ĒśĖņ▓┤Ļ│äņŚÉņä£ ņłśņ¦æļÉ£ ņĀĢļ│┤ņÖĆ ņĄ£ņŗĀ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ£äĒśæ ļÅÖĒ¢źņØä ļČäņäØĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņØ┤ ļ¬®ņĀüņØä ļŗ¼ņä▒ĒĢśĻĖ░ ņØ┤ņĀäņŚÉ ņŗĀņåŹĒ׳ ļīĆņØæĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļÅäļĪØ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņāüĒÖ®Ļ┤Ćļ”¼ ┬Ę ņ×Éņé░ ĒåĄĒĢ®ĒÅēĻ░Ć ┬Ę ņ£äĒśæĻ▓Įļ│┤ ļČäņäØ ļō▒Ļ│╝ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä ņ¦ĆņøÉĒĢśļŖö ņ¦ĆĒ£śĒåĄņĀ£ļź╝ ņĀ£ņĢłĒĢśĻ│Āņ×É ĒĢ£ļŗż.
ļ│Ė ļģ╝ļ¼ĖņØś 2ņןņŚÉņä£ļŖö ļĪØĒ׳ļō£ļ¦łĒŗ┤ņØś ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ēé¼ ņ▓┤ņØĖ ļ░Å MITRE ATT&CK ļ¬©ļŹĖĻ│╝ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ēé¼ ņ▓┤ņØĖ Ļ░£ņäĀ ļ░®ņĢłņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ ļÅÖĒ¢źņØä ņÜöņĢĮĒĢ£ļŗż. 3ņןņŚÉņä£ļŖö MITRE ATT&CK ļ¬©ļŹĖĻ│╝ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ĻĖ░ņłĀ(ņĀäņłĀ, ĻĖ░ļ▓Ģ ļ░Å ņĀłņ░©: Tactics, Techniques and Procedures, ņØ┤ĒĢś TTPs)ņØä ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ēé¼ ņ▓┤ņØĖ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ļŗ©Ļ│äļĪ£ ļČäņäØĒĢśņŚ¼ ņäżļ¬ģĒĢ£ļŗż. 4ņןņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņŚÉ ļīĆņØæĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ£ ļ░®ĒśĖĻĖ░ļŖźņØä ļČäņäØĒĢśĻ│Ā Ļ│ĄĻ▓® ļŗ©Ļ│äļ│äļĪ£ ļīĆņØæĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ£ ļ░®ĒśĖĻĖ░ļŖźņØä ļ¦ĄĒĢæĒĢ£ļŗż. 5ņןņŚÉņä£ļŖö Ļ░£ļ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņÜ┤ņÜ®ņżæņØĖ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ļ░®ĒśĖĻĖ░ļŖźņØä ĒåĄĒĢ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä ņ¦ĆņøÉĒĢśļŖöļŹ░ ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņĀüņØĖ ņ¦ĆĒ£śĒåĄņĀ£ ļ░®ņĢłņØä ņĀ£ņĢłĒĢśĻ│Ā 6ņןņØĆ Ļ▓░ļĪĀĻ│╝ Ē¢źĒøä ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļ░®Ē¢źņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ ņĀ£ņŗ£ĒĢśļŖö ņł£ņ£╝ļĪ£ ļģ╝ļ¼ĖņØä ĻĄ¼ņä▒ĒĢ£ļŗż.
ļ│Ė ņןņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņä£ļĪĀņŚÉņä£ Ļ░äļץĒ׳ ņäżļ¬ģĒĢ£ ļĪØĒ׳ļō£ļ¦łĒŗ┤ ņØś ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ēé¼ ņ▓┤ņØĖ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņĀłņ░©ņÖĆ ļ░®ņ¢┤ņ£ĀĒśĢ, MITREņØś ATT&CK ļ¬©ļŹĖņØä ņåīĻ░£ĒĢśĻ│Ā Ļ│ĄĻ▓® ņøÉņĀÉņ¦Ć ĒāĆĻ▓®ņØä ņ£äĒĢ£ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ēé¼ ņ▓┤ņØĖ ņĀäļץĻ│╝ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ£äĒśæ ļČäņäØ ļ░Å Ļ░£ņäĀ ļ░®ņĢłņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ ļé┤ņÜ®ņØä ņÜöņĢĮĒĢ£ļŗż.
ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ēé¼ ņ▓┤ņØĖ(Cyber Kill Chain)ņØĆ ĻĄ░ņé¼ņĀü Ļ░£ļģÉņØś Ēé¼ ņ▓┤ņØĖ(Kill Chain)ņØä ņĀüņÜ®ĒĢ£ļŗż. ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ļÅä ņØ╝ļĀ©ņØś Ļ│╝ņĀĢņØä Ļ▒░ņ╣śļ®░, ļ░®ņ¢┤ņ×ÉĻ░Ć Ļ│ĄĻ▓® Ļ│╝ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ ĒĢ£ ļŗ©Ļ│äļ¦ī ņ░©ļŗ©ĒĢ┤ļÅä Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņ×ÉĻ░Ć ļŗżņØī Ļ│ĄĻ▓® ļŗ©Ļ│äļĪ£ ņ¦äĒ¢ēņØ┤ ņĀ£ĒĢ£ļÉśļŖö Ļ▓āņŚÉ ņ░®ņĢłĒĢśņŚ¼ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņĀłņ░©ņÖĆ ļ░®ņ¢┤ņ£ĀĒśĢņØä ņĀ£ņŗ£Ē¢łļŗż.
Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņĀłņ░©ļŖö ņĀĢņ░░, ļ¼┤ĻĖ░ĒÖö, ņĀäļŗ¼/ņ£ĀĒż, ņĢģņÜ®, ņäżņ╣ś, ļ¬ģļĀ╣/ņĀ£ņ¢┤, ļ¬®ņĀü ļŗ¼ņä▒ņØś 7ļŗ©Ļ│äļĪ£ Table 1Ļ│╝ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ĻĄ¼ņä▒ļÉ£ļŗż.
Attack procedure of cyber kill chain
ļ░®ņ¢┤ņ£ĀĒśĢņØĆ ļ»ĖĻĄŁ ĒĢ®ņ░Ė ņĀĢļ│┤ņ×æņĀä ĻĄÉļ”¼ ļīĆņØæ ļ░®ņĢłņØä ņĀüņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ░®ņ¢┤ņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņŚÉ ļ¦×ņČżņŗØņ£╝ļĪ£ ļīĆņ▓śĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ĒāÉņ¦Ć, Ļ▒░ļČĆ, ĻĄÉļ×Ć, ņĢĮĒÖö, ĻĖ░ļ¦ī, ĒīīĻ┤┤ņØś 6Ļ░Ćņ¦ĆļĪ£ ĻĄ¼ļČäĒĢśĻ│Ā Table 2ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ņ£ĀĒśĢļ│äļĪ£ ĒÖ£ņÜ®ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ĻĖ░ņłĀņØä ņĀ£ņŗ£Ē¢łļŗż[5].
Cyber kill chain defense types
MITREļŖö ļ»ĖĻĄŁ ņŚ░ļ░®ņĀĢļČĆņØś ņ¦ĆņøÉņØä ļ░øļŖö ļ╣äņśüļ”¼ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼Ļ░£ļ░£ļŗ©ņ▓┤ļĪ£ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ēé¼ ņ▓┤ņØĖņØä ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņ×ÉņØś Ļ░ü Ē¢ēņ£äļōżņØä Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ĻĖ░ņłĀ(TTPs)ļĪ£ ļČäļźśĒĢ£ ATT&CK ļ¬©ļŹĖ[7]ņØä ņĀ£ņĢłĒ¢łļŗż. ņŗżņĀ£ļĪ£ ņØ╝ņ¢┤ļé¼ļŹś ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ļ│ĄĻ▓® ņé¼ļĪĆļź╝ ļČäņäØĒĢśņŚ¼ ņĄ£ņŗĀ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņĀäņłĀĻ│╝ ņ╣©Ēł¼ĻĖ░ņłĀ, ļīĆņØæņĀłņ░© ļō▒ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ£äĒśæ ļ¬©ļŹĖ ļ░Å ļ░®ļ▓ĢļĪĀņØä Ļ░£ļ░£ĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ£ ĒöäļĀłņ×äņøīĒü¼ļź╝ ņĀ£Ļ│ĄĒĢ┤ ņŻ╝Ļ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż.
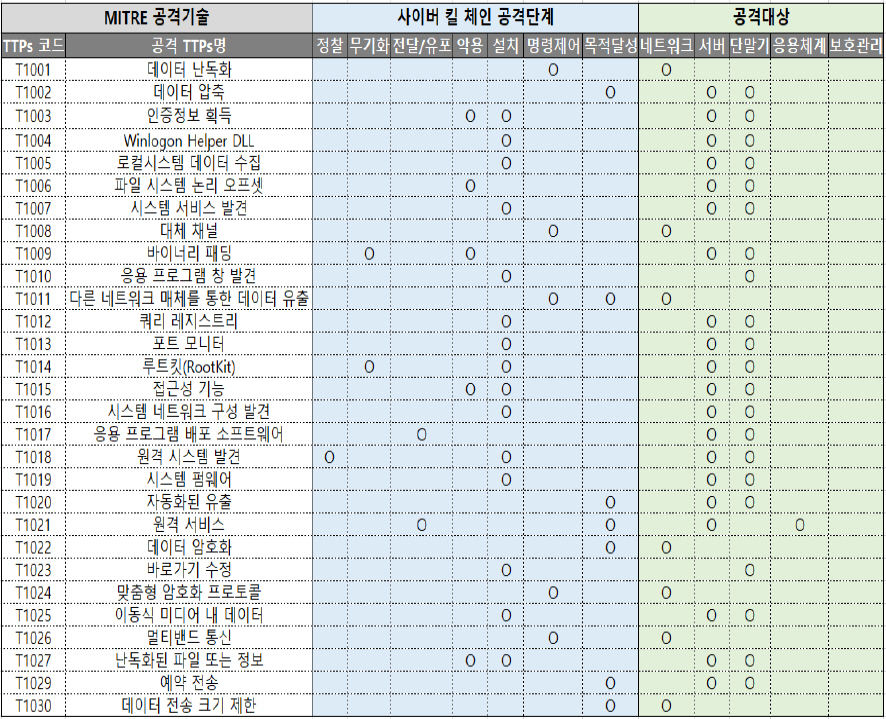
MITRE ATT&CK ļ¬©ļŹĖĻ│╝ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ĻĖ░ņłĀ(TTPs)ņØĆ ņ¦ĆņåŹņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņŚģļŹ░ņØ┤ĒŖĖ ļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳ņ£╝ļ®░, ņÜöņĢĮĒĢśļ®┤ Table 3Ļ│╝ Ļ░Öļŗż[8].
MITRE ATT&CK update summary[8]
ņÜöņĢĮĒĢ£ ļé┤ņÜ®ņØä ĒżĒĢ©ĒĢ┤ 2015ļģäļČĆĒä░ 2020ļģä 10ņøöĻ╣īņ¦Ć ņŚöĒä░ĒöäļØ╝ņØ┤ņ”ł(Windows, MacOS, Linux, Cloud) ļ░Å ļ¬©ļ░öņØ╝(Android, iOS) ĻĖ░ņłĀ, ĒĢ┤Ēé╣ĻĘĖļŻ╣ ļ░Å ņåīĒöäĒŖĖņø©ņ¢┤Ļ░Ć 13ņ░©ļĪĆņŚÉ Ļ▒Ėņ│É ņĀäņ▓┤ ļśÉļŖö ļČĆļČäņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĄ£ņŗĀĒÖöļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż.
ĻĄ░ņé¼ņĀü Ļ░£ļģÉņØś Ēé¼ ņ▓┤ņØĖ(Kill Chain)Ļ│╝ ļÅÖņØ╝ĒĢ£ ņĀłņ░©ņØĖ Ļ░Éņŗ£ņĀĢņ░░(Sensor) ŌĆō Ļ▓░ņŗ¼(Decision) ŌĆō ĒāĆĻ▓®(Strike)ņØś 3ļŗ©Ļ│äņŚÉ ņŚ░ļÅÖņ▓┤Ļ│ä(System of Systems)Ļ░Ć ņČöĻ░ĆļÉ£ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ēé¼ ņ▓┤ņØĖ ņĀäļץņØä ļŗżņØīĻ│╝ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ņĀ£ņŗ£ĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
ņ▓½ņ¦Ė, Ļ░Éņŗ£ņ▓┤Ļ│äļŖö ĒåĄņĀ£ Ļ░ĆļŖźĒĢ£ ļé┤ļČĆ ļäżĒŖĖņøīĒü¼ ļ┐Éļ¦ī ņĢäļŗłļØ╝ ĒåĄņĀ£Ļ░Ć ņĀ£ĒĢ£ļÉśļŖö ņÖĖļČĆ ļäżĒŖĖņøīĒü¼ņŚÉņä£ ĒāÉņ¦ĆļÉśļŖö ņØ┤ņāü(anomaly) ĒśäņāüļÅä ņłśņ¦æĒĢ£ļŗż. ļæśņ¦Ė, Ļ▓░ņŗ¼ņ▓┤Ļ│äļŖö Ļ░üņóģ Ļ░Éņŗ£ņ×Éņé░ņ£╝ļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ ņłśņ¦æļÉśļŖö ļŗżņ¢æĒĢ£ ņĀĢļ│┤ļź╝ ļ╣ģļŹ░ņØ┤Ēä░ ĻĖ░ņłĀļĪ£ ļČäņäØĒĢśņŚ¼ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņØś ņĀĢļŗ╣ņä▒ņØä ĒÖĢļ│┤ĒĢ£ļŗż. ņģŗņ¦Ė, ĒāĆĻ▓®ņ▓┤Ļ│äļŖö ļ¼╝ļ”¼ņĀü ņĀäņ¤üņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒÖĢļīĆļź╝ ļ░®ņ¦ĆĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ņ£äĒŚśņØ┤ ļé«ņØĆ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņøÉņĀÉ ĒāĆĻ▓®Ļ│╝ ņóĆļ╣ä PC Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņ¦ĆņøÉņäĖļĀźĻ╣īņ¦Ć Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ĒĢśļŖö ĒÖĢļīĆ ĒāĆĻ▓® ĻĘĖļ”¼Ļ│Ā ņ£äĒśæĒ¢ēņ£äļź╝ ņäżĻ│äĒĢ£ ņ¦ĆĒ£śņäĖļĀźĻ╣īņ¦Ć ĒżĒĢ©ĒĢ£ ĒāĆĻ▓®ņ£╝ļĪ£ ĻĄ¼ļČäĒĢ£ļŗż. ļ¦łņ¦Ćļ¦ēņ£╝ļĪ£ ļäĘņ¦ĖļŖö Ļ░Éņŗ£ ŌĆō Ļ▓░ņŗ¼ ŌĆō ĒāĆĻ▓® ņ▓┤Ļ│äĻ░Ć ņ£ĀĻĖ░ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ×æļÅÖĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ņŚ░ļÅÖņ▓┤Ļ│äĻ░Ć ĻĄ¼ņČĢļÉśņ¢┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗżĻ│Ā ņĀ£ņŗ£Ē¢łļŗż.
ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ēé¼ ņ▓┤ņØĖņŚÉņä£ ņ¦ĆļŖźĒśĢ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ£äĒśæņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ņØś ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ļ░®ĒśĖņ▓┤Ļ│äņØś ĒĢ£Ļ│äņĀÉņØä ļÅäņČ£ĒĢśĻ│Ā ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ░£ņäĀļÉ£ ļīĆņØæļ░®ņĢłņØä ļŗżņØīĻ│╝ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ņĀ£ņŗ£ĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
ņ¦ĆļŖźĒśĢ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ£äĒśæņØĆ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ļīĆņāüņØś ņ×Āņ×¼ļÉ£ ņé¼ĒÜīĻ│ĄĒĢÖņĀü ņĘ©ņĢĮņĀÉņØä Ļ│ĄļץĒĢśĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ņÜ┤ņÜ®ņżæņØĖ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ļ░®ĒśĖņ▓┤Ļ│äļĪ£ļŖö ļīĆņØæņŚÉ ĒĢ£Ļ│äĻ░Ć ņ׳ņ£╝ļ»ĆļĪ£ ļ░®ņ¢┤Ļ░Ć 100 % ņÖäļ▓ĮĒĢĀ ņłś ņŚåļŗżļŖö ņĀÉņØä ņØĖņĀĢĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗż. ņØ┤ļź╝ Ļ░£ņäĀĒĢśĻ│Ā ļīĆņØæĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ļ░®ĒśĖņ▓┤Ļ│ä ļīĆņ▒ģņØä ņłśļ”ĮĒĢśĻ│Ā ĻĄ¼ņČĢĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗżĻ│Ā Ļ░ĢņĪ░Ē¢łļŗż. ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņØĆ Ļ│äĒÜŹļÉ£ ņŗ£ļéśļ”¼ņśżņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ ņ¦äĒ¢ēļÉśļ®░ ļ¬©ļōĀ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ļŗ©Ļ│äĻ░Ć ņŗżĒ¢ēļÉĀ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ņĄ£ņóģ ļ¬®ņĀüņØ┤ ļŗ¼ņä▒ļÉśļ»ĆļĪ£ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ļ░®ņ¢┤ņØś Ēī©ļ¤¼ļŗżņ×äļÅä ņĢīļĀżņ¦ä Ēī©Ēä┤ĻĖ░ļ░ś ĒāÉņ¦ĆņÖĆ ņ░©ļŗ©ņŚÉņä£ Ļ│ĄĻ▓® ņ▓┤ņØĖ ļČäņäØĻ│╝ ņŚ░Ļ▓░ Ļ│Āļ”¼ ņ░©ļŗ©ņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ░£ņäĀĒĢ£ļŗż. ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ēé¼ ņ▓┤ņØĖ ĻĖ░ļ░śņ£╝ļĪ£ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ļ░®ĒśĖņ▓┤Ļ│äņØś ļīĆņØæļŖźļĀźņØä Ē¢źņāüņŗ£ĒéżĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ņä£ļŖö Ļ│ĄĻ▓® ņżĆļ╣ä ļŗ©Ļ│äņØĖ ļ¼┤ĻĖ░ĒÖöļŗ©Ļ│ä, ļ░®ņ¢┤ ņĖĪļ®┤ņŚÉņä£ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņØä ņ┤łĻĖ░ ļŗ©Ļ│äņŚÉ ņ¦äņĢĢĒĢśļŖöļŹ░ ņŻ╝ņÜöĒĢ£ ņŚŁĒĢĀņØä ĒĢśļŖö ņĢĮĒÖöļŗ©Ļ│ä, Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņØä ļ¼┤ļĀźĒÖöņŗ£Ēé¼ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ĻĖ░ļ¦īļŗ©Ļ│äņŚÉ ļīĆņØæĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ£ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ēé¼ ņ▓┤ņØĖ ņ¦ĆļŖźĒśĢ ļ░®ĒśĖņ▓┤Ļ│ä Ļ░£ņäĀ ļ░®ņĢłņØä ņĀ£ņŗ£Ē¢łļŗż.
Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ļŗ©Ļ│äļŖö ļĪØĒ׳ļō£ļ¦łĒŗ┤ņØś ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ēé¼ ņ▓┤ņØĖņØä ņĀüņÜ®ĒĢśĻ│Ā Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ļŗ©Ļ│äņŚÉ ņĀüņÜ®ļÉ£ ĻĖ░ņłĀņØĆ MITREņŚÉņä£ ņĀ£ņĢłĒĢ£ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ĻĖ░ņłĀ(TTPs)ņØä ĒÖ£ņÜ®ĒĢ£ļŗż.
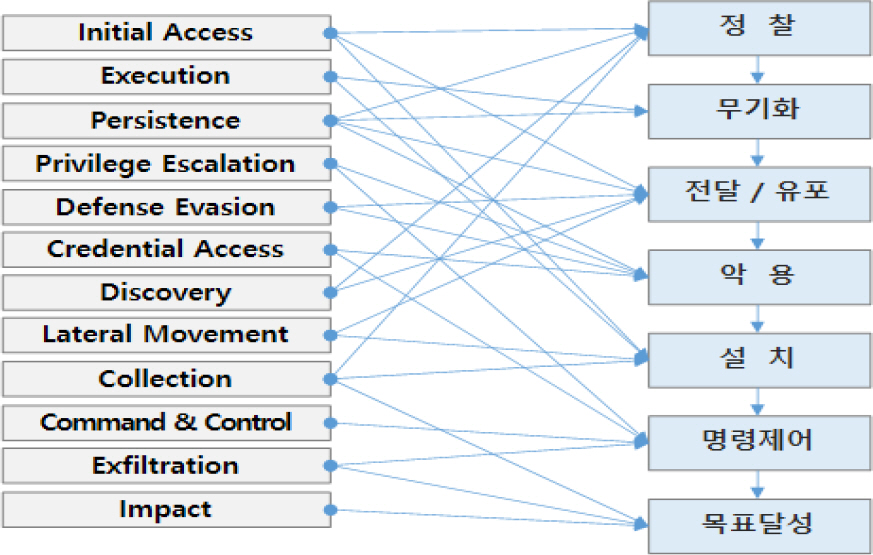
MITREņØś 12Ļ░£ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņśüņŚŁņŚÉ ņåŹĒĢ£ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ĻĖ░ņłĀ(TTPs)ņØśĒŖ╣ņä▒ņØä ĻĖ░ņżĆņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ļŗ©Ļ│äņÖĆ ņŚ░Ļ│äĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ×¼ļČäļźśĒĢ£ Ļ│╝ņĀĢņØĆ Fig. 1Ļ│╝ Ļ░Öņ£╝ļ®░, 2Ļ░£ ņØ┤ņāüņØś Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ļŗ©Ļ│äņŚÉ ņżæļ│ĄļÉśņ¢┤ņĀüņÜ®ļÉ£ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ĻĖ░ņłĀ(TTPs)ļÅä ņ׳ļŗż.
MITREĻ░Ć ņĀäņäĖĻ│ä ĒĢ┤ņ╗ż ĻĘĖļŻ╣ņØś Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ĻĖ░ņłĀ(TTPs)ņØä ļČäņäØĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ£ĀĒśĢĒÖöĒĢ£ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ĻĖ░ņłĀ(TTPs)Ļ│╝ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ēé¼ ņ▓┤ņØĖņØś Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ļŗ©Ļ│ä, Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ļīĆņāüņØä ļČäļźśĒĢśļ®┤ Fig. 2ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ĻĄ¼ņä▒ļÉ£ļŗż.
ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ēé¼ ņ▓┤ņØĖ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ļŗ©Ļ│äļĪ£ ļČäļźśļÉ£ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ĻĖ░ņłĀ(TTPs)ļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ ļ░®ņ¢┤ĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢĀ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ļīĆņāüņØĆ ļäżĒŖĖņøīĒü¼, ņä£ļ▓ä, ļŗ©ļ¦ÉĻĖ░(PC), ņØæņÜ®ņ▓┤Ļ│ä, ļ│┤ĒśĖĻ┤Ćļ”¼ ļō▒ņØś 5Ļ░Ćņ¦ĆļĪ£ ĻĄ¼ļČäĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
MITREņØś Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ĻĖ░ņłĀ(TTPs)ņŚÉ ļīĆņØæĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ£ ļ░®ĒśĖĻĖ░ļŖźņØä ļ░śļō£ņŗ£ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ļīĆņāüņØ┤ ļīĆņØæĒĢĀ ĒĢäņÜöļŖö ņŚåļŗż. ņ”ē, ņä£ļ▓äņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ĻĖ░ņłĀ(TTPs)ņØ┤ ļ░śļō£ņŗ£ ņä£ļ▓äņŚÉņä£ļ¦ī ļīĆņØæĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ņØśļ»ĖĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØĆ ņĢäļŗłļ®░, ņä£ļ▓äņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņØä ņé¼ņĀäņŚÉ ļäżĒŖĖņøīĒü¼ņŚÉņä£ ļīĆņØæĒĢśĻ▒░ļéś ņØæņÜ®ņ▓┤Ļ│ä ļ░Å ļ│┤ĒśĖĻ┤Ćļ”¼ Ļ┤ĆņĀÉņŚÉņä£ ļīĆņØæĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗżļŖö ņØśļ»ĖņØ┤ļŗż.
ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņŚÉ ļīĆņØæĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ£ ļ░®ĒśĖĻĖ░ļŖźņØĆ MITREņØś ĒāÉņ¦Ć, Ļ▒░ļČĆ, ĻĄÉļ×Ć, ņĢĮĒÖö, ĻĖ░ļ¦ī, ĒīīĻ┤┤ņØś 6Ļ░Ćņ¦Ć ļ░®ņ¢┤ņ£ĀĒśĢĻ│╝ Ļ░ü ĻĖ░ļŖźņØä ĒåĄĒĢ®ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ņ¦ĆĒ£śĒåĄņĀ£ļź╝ ņČöĻ░ĆĒĢśņŚ¼ Table 4ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ļČäļźśĒĢ£ļŗż.
Protection function according to defense type
ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ļ░®ĒśĖĻĖ░ļŖźņØĆ 2019ļģäņŚÉ ĻĄŁļé┤ 473Ļ░£ ņŚģņ▓┤Ļ░Ć ņĀĢļ│┤ļ│┤ņĢł ņŗ£ņŖżĒģ£ņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ░£ļ░£ĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņāüņÜ®ĒÖöļÉ£ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ļ░®ĒśĖņ▓┤Ļ│äĻ░Ć Ļ░Ćņ¦ĆĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŖö Ļ│ĄĒåĄļÉ£ ĒĢĄņŗ¼ĻĖ░ļŖźņØä ĻĖ░ņżĆņ£╝ļĪ£ ļÅäņČ£ĒĢ£ļŗż. ņĀĢļ│┤ļ│┤ĒśĖņé░ņŚģņØś ĒŖ╣ņä▒ņāü ņĀ£ĒÆłĻ│╝ ņä£ļ╣äņŖżņØś ĒåĄĒĢ® ļ░Å ņ£ĄĒĢ®ņØĆ ļ¦żņÜ░ ļ╣Āļź┤Ļ▓ī ņ¦äĒ¢ēļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳ņ¢┤ ļČäļźś ĻĖ░ņżĆņØä Ļ│╝Ļ▒░ņØś ĒĢśļō£ņø©ņ¢┤, ņåīĒöäĒŖĖņø©ņ¢┤, ņä£ļ╣äņŖżņØś 3Ļ░Ćņ¦Ć ļČäņĢ╝ļĪ£ ĻĄ¼ļČäĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØĆ ļ¬©ĒśĖĒĢ┤ņĪīļŗż. ĻĘĖļלņä£ ĒĢ£ĻĄŁņĀĢļ│┤ļ│┤ĒśĖņé░ņŚģĒśæĒÜī(KISIA)ņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņĀĢļ│┤ļ│┤ĒśĖņé░ņŚģ Ļ┤ĆļĀ© ĒĢÖĻ│ä ļ░Å ņé░ņŚģĻ│äņØś ņĀäļ¼ĖĻ░ĆļōżļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ ņāüņÜ®ĒÖöļÉ£ ņĀ£ĒÆłņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņŗ¼ņĖĄņĀüņØĖ ņĪ░ņé¼ļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņĀĢļ│┤ļ│┤ĒśĖņé░ņŚģņØä ņ×¼ļČäļźśĒ¢łļŗż. ĻĘĖ ņżæņŚÉņä£ ņĀĢļ│┤ļ│┤ņĢł ņŗ£ņŖżĒģ£ņØś ĻĄ¼ņä▒ņØä ļ░®ņ¢┤ņ£äņ╣ś ĻĖ░ņżĆņ£╝ļĪ£ ļäżĒŖĖņøīĒü¼ļ│┤ņĢł, ņŗ£ņŖżĒģ£ļ│┤ņĢł(PC ĒżĒĢ©), ņĀĢļ│┤ņ£ĀņČ£ļ░®ņ¦Ć, ņĢöĒśĖ/ņØĖņ”Ø, ļ│┤ņĢłĻ┤Ćļ”¼ 5Ļ░Ćņ¦ĆļĪ£ ļČäļźśĒĢśĻ│Ā Table 5ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ļ░®ĒśĖĻĖ░ļŖźņØä ņŗØļ│äĒĢ£ļŗż[11].
Identification of protection functions by protection target
ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ēé¼ ņ▓┤ņØĖņØś Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņĀłņ░© ļ░Å ļ░®ņ¢┤ņ£ĀĒśĢņØä ĻĖ░ņżĆņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ĻĖ░ņłĀ(TTPs)ņŚÉ ļīĆņØæĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ£ ļ░®ĒśĖĻĖ░ļŖźņØä ņāüņÜ®ĒÖöļÉ£ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ļ░®ĒśĖņ▓┤Ļ│äņŚÉņä£ ņŗØļ│äĒĢśņśĆļŗż. Table 6Ļ│╝ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ēé¼ ņ▓┤ņØĖņŚÉ ĻĖ░ļ░śĒĢ£ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ļ░®ĒśĖņ▓┤Ļ│äļź╝ ļ¦ĄĒĢæĒĢ£ļŗż.
Cyber kill chain based cyber protection functional product analysis
ņĢīļĀżņ¦Ćņ¦Ć ņĢŖņØĆ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ£äĒśæ ņżæ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ļ░®ĒśĖņ▓┤Ļ│äņŚÉņä£ ņÜ░ņŚ░ĒĢśĻ▓ī ĒāÉņ¦ĆļÉ£ ĒĢśļéśņØś ņ£äĒśæ ņĀĢļ│┤ļź╝ ĻĖ░ņżĆņ£╝ļĪ£ Ēö╝ĒĢ┤ļź╝ ļČäņäØĒĢśĻ│Ā ļīĆņØæņ▒ģņØä ĒīÉļŗ©ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØĆ ņĀ£ĒĢ£ļÉ£ ņĀĢļ│┤ļĪ£ ņØĖĒĢ┤ ņלļ¬╗ļÉ£ ņāüĒÖ® ĒīÉļŗ©ņØä ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż.
ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ņלļ¬╗ļÉ£ ĒīÉļŗ©ņØä ļ│┤ņÖäĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ņŗĀĻĘ£ļĪ£ ĒāÉņ¦ĆļÉ£ ņ£äĒśæņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ ņåīĻ┤Ć ļäżĒü¼ņøīĒü¼ ĒÖśĻ▓ĮņŚÉņä£ ņÜ┤ņÜ®ņżæņØĖ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ļ░®ĒśĖņ▓┤Ļ│ä, ņŗ£ņŖżĒģ£, ļäżĒŖĖņøīĒü¼ņןļ╣ä ļō▒ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ×Éņé░ņŚÉņä£ Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ļÉ£ ņĀĢļ│┤ļź╝ ņĄ£ļīĆĒĢ£ ņłśņ¦æĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ£äĒśæ ņśüĒ¢źļÅäļź╝ ļČäņäØĒĢśĻ│Ā ļīĆņØæņ▒ģņØś ņÜ░ņäĀņł£ņ£äļź╝ ņ×ÉļÅÖņ£╝ļĪ£ ņČöņ▓£ĒĢ┤ ņŻ╝Ļ▒░ļéś ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņ¦ĆĒ£śĻ▓░ņŗ¼ ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļÅäļĪØ ņ¦ĆņøÉĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ļŗżņØīĻ│╝ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņ¦ĆĒ£śĒåĄņĀ£Ļ░Ć ĒĢäņÜöĒĢśļŗż.
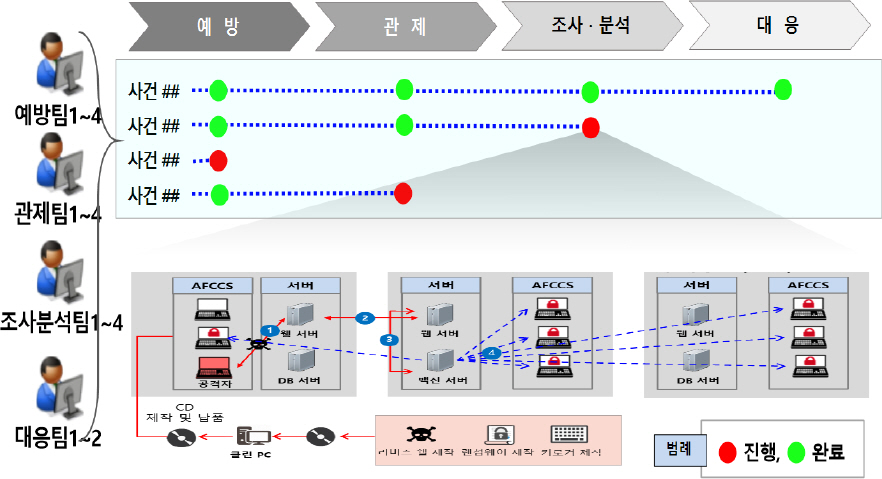
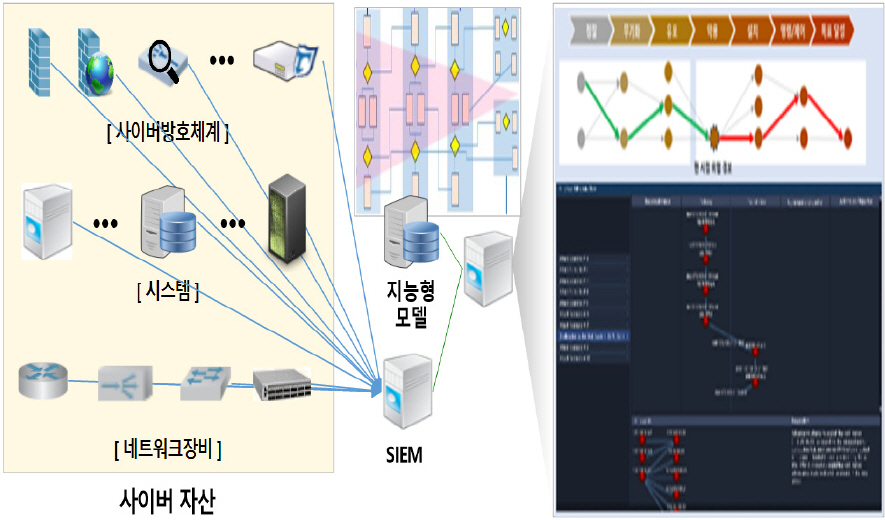
ņśłļ░®, Ļ┤ĆņĀ£, ņĪ░ņé¼ļČäņäØ, ļīĆņØæ ļō▒ Ēśäņ×¼ ņ¦äĒ¢ēņżæņØ┤Ļ▒░ļéś ņÖäļŻīļÉ£ ļ¬©ļōĀ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņāüĒÖ®ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ ņŚģļ¼┤ļ│ä ņ¦äĒ¢ē ņāüĒÖ®ņØä ņŗżņŗ£Ļ░äņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØĖņŗØĒĢśĻ│Ā ņāüĒÖ®ĒÅēĻ░Ć, ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢ, ņŚģļ¼┤ĒåĄņĀ£ ļō▒ ĒåĄĒĢ®ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņŗ£Ļ░üĒÖöĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņāüĒÖ®Ļ┤Ćļ”¼ņ▓┤Ļ│äļź╝ Fig. 3Ļ│╝ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ĻĄ¼ņČĢĒĢ£ļŗż[12]. ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņāüĒÖ® ļ░Å ņ£äĒśæņāüĒÖ®ņØä ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØĖņŗØĒĢśĻ│Ā ņŗĀņåŹ┬ĘņĀĢĒÖĢĒĢ£ ņāüĒÖ®ĒīÉļŗ©ņØä ĒåĄĒĢ£ ņĄ£ņĀüņØś ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ¦üļ®┤ĒĢ£ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ£äĒśæņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ ļ¦×ņČżņŗØ ļīĆņØæņŚŁļ¤ēņØä Ļ░ĢĒÖöĒĢ£ļŗż.
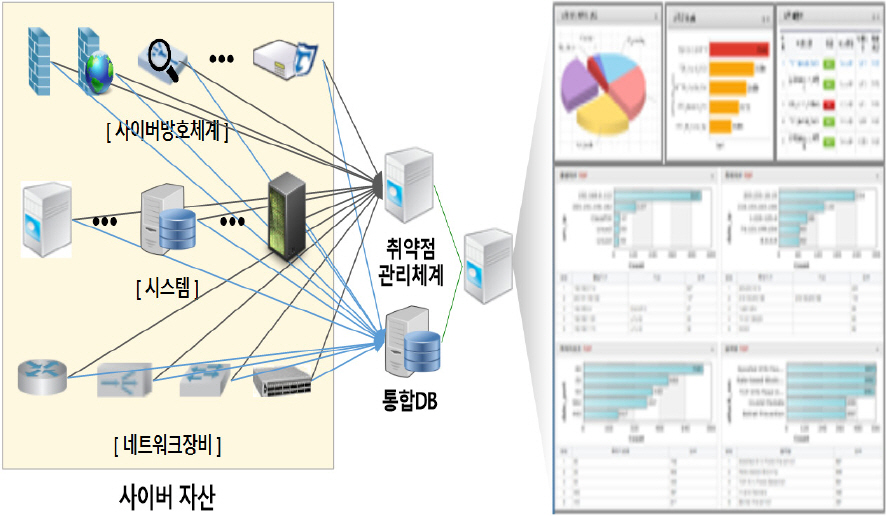
ļäżĒŖĖņøīĒü¼ņāüņŚÉņä£ ņÜ┤ņÜ®ņżæņØĖ ļ¬©ļōĀ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ×Éņé░ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ ņ×ÉļÅÖņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØĖņŗØĒĢśĻ│Ā ļÅÖņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│ĆļÅÖļÉśļŖö ņ×Éņé░ ņĀĢļ│┤ļź╝ ņŻ╝ĻĖ░ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĄ£ņŗĀĒÖöĒĢśņŚ¼ ņŗ£Ļ░üĒÖöĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ×Éņé░ ĒåĄĒĢ®ĒÅēĻ░Ćņ▓┤Ļ│äļź╝ Fig. 4ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ĻĄ¼ņČĢĒĢ£ļŗż[12]. ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ļ░®ĒśĖņ▓┤Ļ│ä, ņŗ£ņŖżĒģ£, ļäżĒŖĖņøīĒü¼ņןļ╣ä ļō▒ ļ¬©ļōĀ ņ×Éņé░ņØś ĻĖ░ļ│Ė ņĀ£ņøÉĻ│╝ ņŚģļŹ░ņØ┤ĒŖĖ ņĀĢļ│┤, ņŗØļ│äļÉ£ ņĘ©ņĢĮņĀÉ ņĀĢļ│┤Ļ╣īņ¦Ć ļŹ░ņØ┤Ēä░ļ▓ĀņØ┤ņŖżļĪ£ ĻĄ¼ņČĢĒĢśņŚ¼ ņŗżņŗ£Ļ░ä Ļ░Ćņŗ£ĒÖöļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ×Éņé░ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņāüĒā£ĒÅēĻ░Ć ļ░Å ņĘ©ņĢĮņĀÉ Ļ┤Ćļ”¼ņŚŁļ¤ēņØä Ļ░ĢĒÖöĒĢ£ļŗż.
ļ░®ĒÖöļ▓Į, IPS, ņø╣ļ░®ĒÖöļ▓Į, APTļīĆņØæ, ļ░öņØ┤ļ¤¼ņŖżļ░®ņŚŁņ▓┤Ļ│ä Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ļ░®ĒśĖņ▓┤Ļ│äņÖĆ ļØ╝ņÜ░Ēä░, ļ░▒ļ│Ė ļō▒ ļäżĒŖĖņøīĒü¼ņןļ╣äņŚÉņä£ ĒāÉņ¦ĆļÉ£ ļ¬©ļōĀ ņ£äĒśæ ņĀĢļ│┤ļŖö SIEMņ£╝ļĪ£ ņóģĒĢ®ĒĢ£ļŗż. ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ£äĒśæĻ▓Įļ│┤ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņāüĻ┤ĆĻ┤ĆĻ│äļź╝ ņ¦ĆļŖźĒśĢļ¬©ļŹĖņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ Ļ│ĄĻ▓® Ļ▓ĮļĪ£ļź╝ ņ×ÉļÅÖņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĀ£Ļ│ĄĒĢśĻ│Ā, Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ĻĖ░ņłĀ(TTPs)ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļīĆņØæņ▒ģņØä ĒÅēĻ░Ć ļ░Å ņÜ░ņäĀņł£ņ£äļź╝ ņČöņ▓£ ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ£äĒśæĻ▓Įļ│┤ ļČäņäØņ▓┤Ļ│äļź╝ Fig. 5ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ĻĄ¼ņČĢĒĢ£ļŗż[12]. ņŗ¼ņĖĄļČäņäØļÉ£ ņ£äĒśæ ņĀĢļ│┤ļź╝ ļ░öĒāĢņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ│ĄĻ▓® Ļ▓ĮļĪ£ļź╝ ĻĄ¼ņä▒ĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņłśņ¦æļÉ£ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ£äĒśæĻ░ä ņŚ░Ļ┤ĆĻ┤ĆĻ│äļź╝ ļČäņäØĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ░£ņāØ Ļ░ĆļŖźĒĢ£ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ£äĒśæņāüĒÖ®ļź╝ ņŗ£Ļ░üĒÖöĒĢśņŚ¼ ņĀ£Ļ│ĄĒĢ£ļŗż. ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ£äĒśæņāüĒÖ®ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņĄ£ņĀüņØś ļīĆņØæņ▒ģņØä ņČöņ▓£ĒĢśĻ│Ā ļīĆņØæĻ▓░Ļ│╝ ļČäņäØ ļ░Å Ēö╝ļō£ļ░▒ņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ£äĒśæ ļČäņäØņŚŁļ¤ēņØä Ļ░ĢĒÖöĒĢ£ļŗż.
ļ│Ė ļģ╝ļ¼ĖņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļīĆņØæņŚŁļ¤ēņØä Ļ│ĀļÅäĒÖöĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ļĪØĒ׳ļō£ļ¦łĒŗ┤ņØś ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ēé¼ ņ▓┤ņØĖĻ│╝ MITRE ATT&CK ļ¬©ļŹĖņØä ĻĖ░ļ░śĒĢ£ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ļ░®ĒśĖĻĖ░ļŖźņØä ĒåĄĒĢ® ļČäņäØĒĢśņŚ¼ ņäĀņĀ£ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ£äĒśæņØä ņśłņĖĪĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņŗĀņåŹĒĢ£ Ļ▓░ņŗ¼ ļ░Å ļīĆņØæņØ┤ Ļ░ĆļŖźĒĢ£ ņ¦ĆĒ£śĒåĄņĀ£ļź╝ ņĀ£ņĢłĒ¢łļŗż.
ņŚ░Ļ┤Ć ļČäņäØņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ņä£ļŖö 1Ļ░£ņØś Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ĻĖ░ņłĀ(TTPs)ņØ┤ 2Ļ░£ ņØ┤ņāüņØś ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ēé¼ ņ▓┤ņØĖ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ļŗ©Ļ│äņŚÉ ņØ╝ļČĆ ņĀüņÜ®ļÉśņŚłĻ│Ā, ļśÉĒĢ£, 1Ļ░£ņØś Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ĻĖ░ņłĀ(TTPs)ņŚÉ ļīĆņØæĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ£ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ļ░®ĒśĖĻĖ░ļŖźņØĆ 1Ļ░£ ņØ┤ņāü ņĪ┤ņ×¼ĒĢśļ®░, ļ░®ņ¢┤ņ£ĀĒśĢĻ│╝ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ļ░®ĒśĖņ▓┤Ļ│äĻ░Ć ļŗżņ¢æĒĢśĻ▓ī ļČäĒżļÉ©ņØä ĒÖĢņØĖĒ¢łļŗż.
Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ĻĖ░ņłĀ(TTPs)ņŚÉ ļīĆņØæĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ£ ļ░®ĒśĖĻĖ░ļŖźņØ┤ ĒÖĢņØĖļÉśņŚłņ¦Ćļ¦ī, ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņØĆ ņ¦ĆļŖźĒÖö ┬Ę Ēæ£ņĀüĒÖö ┬Ę Ļ│ĀļÅäĒÖö ┬Ę ņĪ░ņ¦üĒÖöļÉśņ¢┤ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ĻĖ░ņłĀ(TTPs)ņØ┤ ĒĢśļŻ©Ļ░Ć ļŗżļź┤Ļ▓ī ĻĖēņåŹļÅäļĪ£ ļ░£ņĀäņżæņØ┤ļ»ĆļĪ£ ņ¦ĆņåŹņĀüņØĖ ĻĄŁļé┤ ┬Ę ņÖĖ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ļ│ĄĻ▓®Ļ│╝ ņ£äĒśæ ņé¼ļĪĆļź╝ ļČäņäØĒĢśņŚ¼ ņĢīļĀżņ¦Ćņ¦Ć ņĢŖņØĆ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ£äĒśæņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļ░®ĒśĖĻĖ░ļŖźņØä ĒÖĢļ│┤ĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ│Ė ļģ╝ļ¼ĖņŚÉņä£ ņĀ£ņĢłĒĢ£ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ņ¦ĆĒ£śĒåĄņĀ£ņŚÉ ņŚ░ļÅÖĒĢĀ ĒĢäņÜöĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŗż.
Ē¢źĒøäņŚÉļŖö Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ĻĖ░ņłĀ(TTPs)ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ MITREĻ░Ć ņĀ£ņĢłĒĢ£ ļ░®ņ¢┤ĻĖ░ļŖź(Mitigation ID)ņØä ĻĖ░ļ░śņ£╝ļĪ£ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä Ēé¼ ņ▓┤ņØĖ Ļ│ĄĻ▓®ņĀłņ░©ņÖĆ ļ░®ņ¢┤ņ£ĀĒśĢņ£╝ļĪ£ ņäĖļČäĒÖöĒĢśĻ│Ā ņÜ┤ņÜ®ņżæņØĖ ļ░®ĒśĖĻĖ░ļŖźĻ│╝ ņŚ░Ļ┤Ćņä▒ ļČäņäØņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņé¼ņØ┤ļ▓ä ļ░®ĒśĖņ▓┤Ļ│äņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļ░®ĒśĖņłśņżĆņØä ņĀ£ņŗ£ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļÅäļĪØ ĒĢ£ļŗż.
REFERENCES
[1] Government of the Republic of Korea. National Cyber Security Master Plan, pp. 2September, 2019.
[2] Seho Choi et al, "A study on Defense Indicators for Evaluation of Defense Cyber Response System," 2019 KIMST an Academic Conference for Estimating, pp. 646ŌĆō647, November, 2019.
[3] Kevin Daimi, "Computer and Network Security Essentials," Springer International Publishing, p. 585ŌĆō602, 2018.
[4] Eric M. Hutchins et al, "Intelligence-Driven Computer Network Defense Informed by Analysis of Adversary Campaigns and Intrusion Kill Chains," Proc. 6th ICIW 11 Academic Conferences, Ltd., pp. 113ŌĆō125, 2010.
[5] U.S. Joint Chief of Staff. Information Operation Doctrine(JP3-13), November, 2012.
[6] The MITRE Corporation. MITRE ATT&CK, Accessed Match 21, 2021.https://attack.mitre.org.
[7] Blake E. Storm, Andy Appleaum, Doug P. Miler, Kathryn C. Nickels, Adam G. Pennington and Cody B. Thomas, "MITRE ATT&CKTM: Design and Philosophy," MITRE Corporation, June, 2018.
[8] The MITRE Corporation. MITRE ATT&CK, Accessed Match 30, 2021.https://attack.mitre.org/resources/updates/.
[9] Jea-woo Yoo and Dae-woo Park, "Cyber Kill Chain Strategy for Hitting Attacker Origin," Jornal of the Korea Institute of Information and Communication Engineering, Vol. 21, No. 11, November, 2019.
[10] Sun-Jae Lee et al, "A Study on the Analysis and Enhancement for Cyber Security," The Korea Association For Industrial Security, Vol. 9, No. 1, pp. 69ŌĆō91, June, 2019.
[11] Korea Information Security Industry Association. 2019. "Survey for Information Security Industry in Korea," Korea Information Security Industry Association, 9th Floor, 135, Jungdae-ro, Songpa-gu, Seoul, Republic of Korea, p. 14p. 149ŌĆō158.
[12] Republic of Korea Ministry of National Defense. 2019. "2019 ŌĆō 2033 Defense Informatization Basic Plan," Republic of Korea Ministry of National Defense, 22, Itaewon-ro, Yongsan-gu, Seoul, Republic of Korea, p. 84ŌĆō88.
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- 2,761 View
- 17 Download
- Related articles in J. KIMS Technol.
-
A Study on Configuration Design of the 2D Course Correction Munition2008 August;11(4)